|
I am currently working in the Large Language Model Department at Tencent (Hunyuan team). I received my Master's degree from the Institute of Information Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, where I was advised by Prof. Zheng Lin. Previously, I was a research intern at the Meituan NLP Center and the Pattern Recognition Center (PRC) at WeChat AI (under the supervision of Fandong Meng) from 2021 to 2022. My research interests include Long-Context LLMs, dialogue generation, and related applications. Please reach out to me via email: wlanrui@bupt.cn. |

|
|
|
(*: Equal contribution) |

|
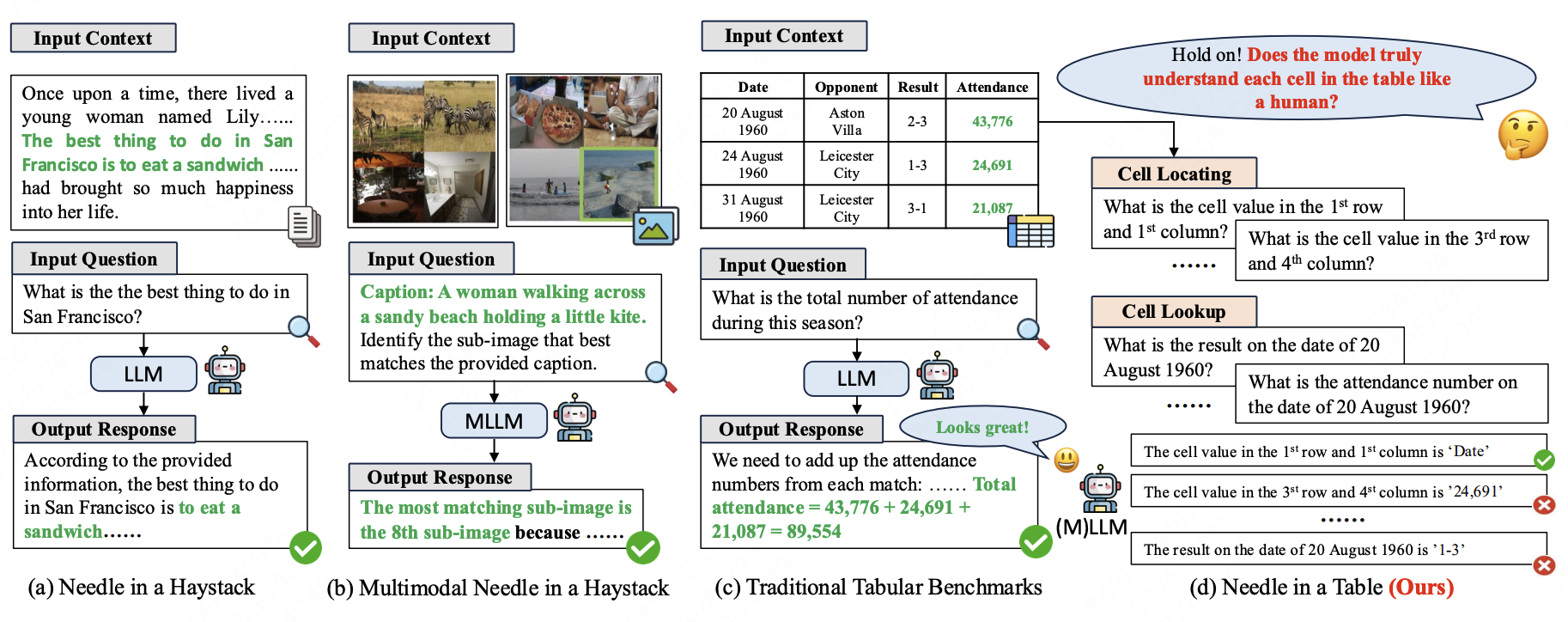
Lanrui Wang, Mingyu Zheng, Hongyin Tang, Zheng Lin, Yanan Cao, Jingang Wang, Xunliang Cai, Weiping Wang NeurIPS, 2025 pdf / code Processing structured tabular data, particularly large and lengthy tables, constitutes a fundamental yet challenging task for large language models (LLMs). However, existing long-context benchmarks like Needle-in-a-Haystack primarily focus on unstructured text, neglecting the challenge of diverse structured tables. Meanwhile, previous tabular benchmarks mainly consider downstream tasks that require high-level reasoning abilities, and overlook models' underlying fine-grained perception of individual table cells, which is crucial for practical and robust LLM-based table applications. To address this gap, we introduce \textsc{NeedleInATable} (NIAT), a new long-context tabular benchmark that treats each table cell as a ``needle'' and requires models to extract the target cell based on cell locations or lookup questions. Our comprehensive evaluation of various LLMs and multimodal LLMs reveals a substantial performance gap between popular downstream tabular tasks and the simpler NIAT task, suggesting that they may rely on dataset-specific correlations or shortcuts to obtain better benchmark results but lack truly robust long-context understanding towards structured tables. Furthermore, we demonstrate that using synthesized NIAT training data can effectively improve performance on both NIAT task and downstream tabular tasks, which validates the importance of NIAT capability for LLMs' genuine table understanding ability. Our data, code and models will be released to facilitate future research. |

|
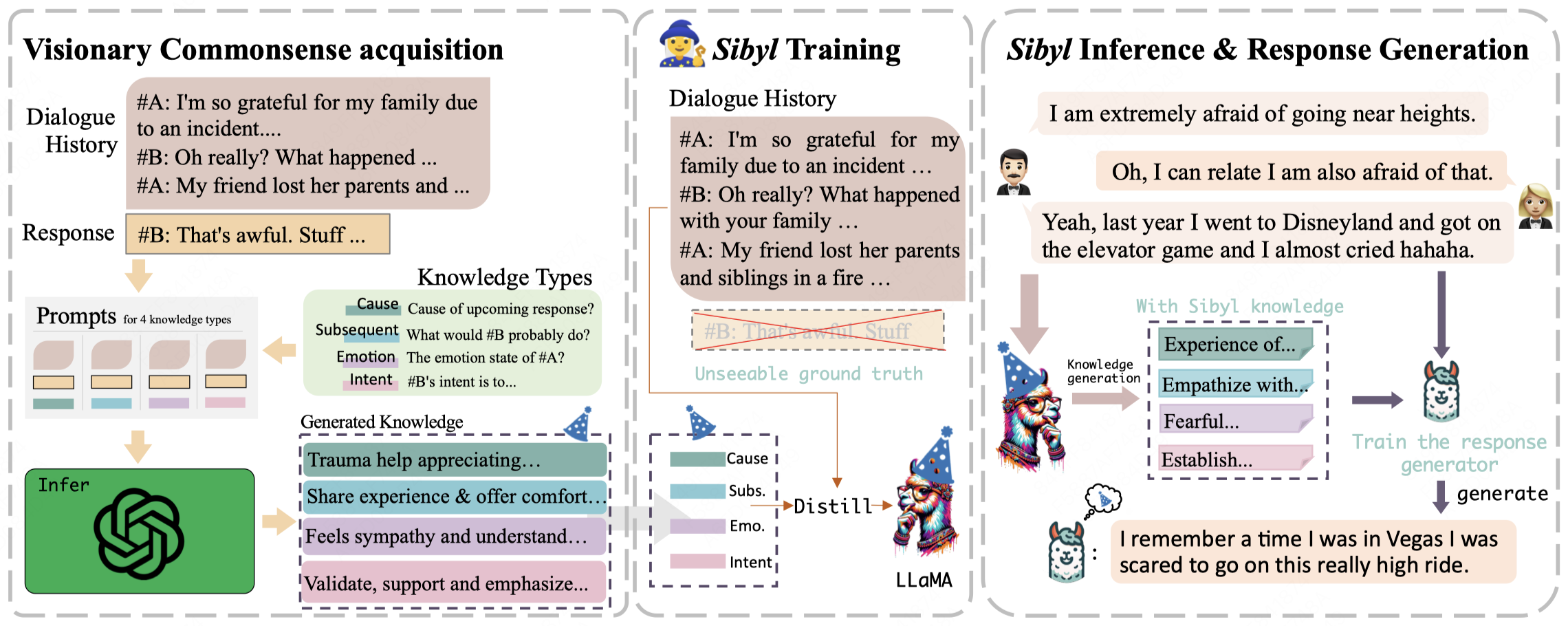
Lanrui Wang, Jiangnan Li*, Chenxu Yang, Zheng Lin, Hongyin Tang, Huan Liu, Yanan Cao, Jingang Wang, Weiping Wang COLING, 2025 pdf / code Current commonsense knowledge derived from dialogue contexts is inherently limited and often fails to adequately anticipate the future course of a dialogue. This lack of foresight can mislead LLMs and hinder their ability to provide effective support. In response to this challenge, we present an innovative framework named Sensible and Visionary Commonsense Knowledge (Sibyl). |

|
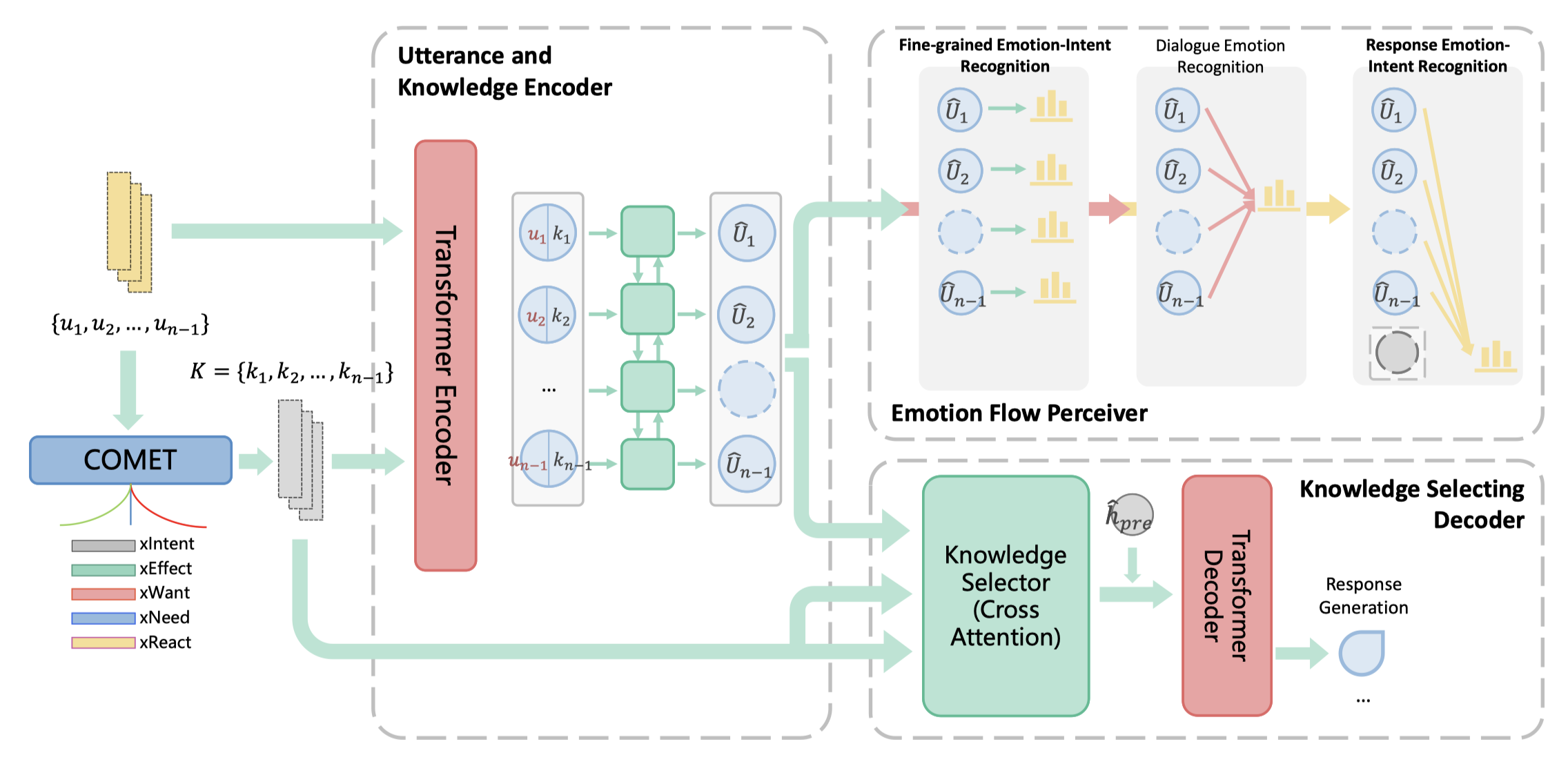
Lanrui Wang, Jiangnan Li, Zheng Lin, Fandong Meng, Chenxu Yang, Weiping Wang, Jie Zhou EMNLP, 2022 (Findings) pdf / code For Empathetic Dialogue Generation task, emotions change dynamically between utterances, which makes previous works difficult to perceive the emotion flow and predict the correct emotion of the target response, leading to inappropriate response. In this work, we improved not only the ability to recognize contextual emotions, but also the ability to filter out unreasonable external knowledge, allowing the model to generate more sensible empathetic responses. |
|
Design and source code from Jon Barron's website |